Online Encyclopedia
Iraq
The Republic of Iraq is a Middle Eastern country in southwestern Asia encompassing the ancient region of Mesopotamia. It shares borders with Saudi Arabia and Kuwait to the south, Turkey to the north, Syria to the north-west, Jordan to the west and Iran to the east. Its current leadership was put in place June 28, 2004, following a March 2003 invasion, led by US and UK forces, that drove Saddam Hussein from power.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contents |
History
Main article: History of Iraq
The fertile area of Mesopotamia, between the Euphrates and the Tigris rivers, was the birth place of several of the world's oldest civilisations, such as the Sumerians, Akkadians, Aramean Babylonians and Aramean Assyrians. Absorbed by the Persian and the Seleucid Empires for several centuries, Mesopotamia was conquered by the Arabs in 656, and in 762 the Caliphate was moved to the new city of Baghdad (near ancient Babylon). This city remained one of the centers of the Arab world until it was incorporated into the Ottoman Empire in 1534.
The Ottoman Empire's entry into World War I proved to be disastrous, as the conclusion of that war in 1918 culminated in the Treaty of Sèvres and the Treaty of Lausanne that shattered the Empire into independent countries. These treaties enacted the provisions of the wartime Sykes-Picot Agreement, under which France was to be given control of Syria and Lebanon, while the United Kingdom received Palestine and Iraq, the latter having been seized in 1915. Under a League of Nations mandate, the UK retained control until Iraq gained independence in 1932.
The monarchy was overthrown in 1958, and the name of the country was changed to the "Republic of Iraq". The Ba'ath Party gained control in 1968, and established a strict rule, notably after the ascent to power of Saddam Hussein in 1979. In the 1980s, Iraq was involved in a long war with neighbour Iran, ending in 1988.
Following Iraq's occupation of Kuwait in 1990, and the subsequent expulsion by international troops, Iraq was internationally isolated until the spring of 2003 when, following attempts by the UN to resume weapons inspections and a perceived threat of weapons proliferation, the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia, Denmark and Poland controversially invaded Iraq and removed the Ba'ath Party from power. Spain's army participated in the occupation of Iraq after invasion was completed. After a period of military occupation, the coalition nominally transferred sovereignty to the interim Iraqi government on Monday, June 28, 2004 at 10:26 AM local time. More than 160,000 Coalition soldiers plus an additional 20,000 "Private military contractors" remain in the country.
See also: Reconstruction of Iraq
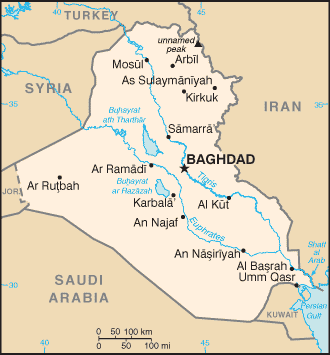
Provinces
Main article: Provinces of Iraq
Iraq is divided into 18 provinces (muhafazat, singular - muhafazah):
- Al Anbar
- Al Basrah
- Al Karbala
- Al Muthanna
- Al Qadisyah
- An Najaf
- Arbil
- As Sulaymaniyah
- At Ta'mim
- Babil
- Baghdad
- Dahuk
- Dhi Qar
- Diyala
- Maysan
- Ninawa
- Salah ad Din
- Wasit
Geography
Main article: Geography of Iraq
Large parts of Iraq consist of desert, but the area between the two major rivers Euphrates and Tigris is fertile, with the rivers carrying about 60 million cubic meters of silt annually to the delta. The north of the country is largely mountainous, with the highest point being Haji Ibrahim at 3,600 m. Iraq has a small coastline with the Persian Gulf. Close to the coast and along the Shatt al-Arab there used to be marshlands, but many of these were drained in the 1990s.
The local climate is mostly a desert clime with mild to cool winters and dry, hot, cloudless summers. The northern mountainous regions experience cold winters with occasional heavy snows, sometimes causing extensive flooding. The capital Baghdad is situated in the centre of the country, on the banks of the Tigris. Other major cities include Basra in the south and Mosul in the north. Iraq is considered to be one of the fifteen lands that comprise the so-called "Cradle of Humanity".
Economy
Main article: Economy of Iraq
Iraq's economy is dominated by the oil sector, which has traditionally provided about 95% of foreign exchange earnings. In the 1980s financial problems caused by massive expenditures in the eight-year war with Iran and damage to oil export facilities by Iran led the government to implement austerity measures, borrow heavily, and later reschedule foreign debt payments; Iraq suffered economic losses from the war of at least $100 billion. After hostilities ended in 1988, oil exports gradually increased with the construction of new pipelines and restoration of damaged facilities.
Iraq's seizure of Kuwait in August 1990, subsequent international economic sanctions, and damage from military action by an international coalition beginning in January 1991 drastically reduced economic activity. Although government policies supporting large military and internal security forces and allocating resources to key supporters of the Ba`ath Party government have hurt the economy, implementation of the United Nations' oil-for-food programme in December 1996 has helped improve conditions for the average Iraqi citizen. For the first six, six-month phases of the programme, Iraq was allowed to export limited amounts of oil in exchange for food, medicine, and some infrastructure spare parts.
In December 1999 the UN Security Council authorised Iraq to export under the program as much oil as required to meet humanitarian needs. Oil exports were more than three-quarters of the pre-war level. However, 28% of Iraq's export revenues under the programme are deducted to meet UN Compensation Fund and UN administrative expenses. The drop in GDP in 2001 was largely the result of the global economic slowdown and lower oil prices. Following the 2003 invasion of Iraq the economy has to a great extent shut down and attempts are underway to revive it from the damages of the war and rampant crime.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Iraq
Almost 75% of Iraq's population consists of Arabic speakers (mainly Iraqi but some Hejazi); the other major ethnic group are the Kurds (20%), who live in the north and north-east of the country. Other distinct groups are Turkomans, East Arameans (consisting of Christian Assyrians and Mandean Babylonians), Iranians, Lurs, Armenians and Yezidis (possible dessendants of the ancient Sumerian culture). Arabic is the official language, although Kurdish has an official status in the North and English is the most commonly spoken Western language. East Aramaic is also used by the country's Aramean population. More than 40% of the Iraqi population is under the age of 15.
Most Arab Iraqi Muslims are members of the Shiite sect, but there is a large Sunni population as well, made up of both Arabs and Kurds. Small communities of Christians, Bahá'ís, Mandaeans, and Yezidis also exist. Most Kurds are Sunni Muslim but differ from their Arab neighbours in language, dress, and customs.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Iraq
Miscellaneous topics
- 2004 in Iraq
- Communications of Iraq
- Transportation in Iraq
- Military of Iraq
- Foreign relations of Iraq
- List of Kings of Iraq
- List of Presidents of Iraq
- List of Prime Ministers of Iraq
- Human rights violations in Iraq
- List of places in Iraq
- 2003 Invasion of Iraq
- Arab Tribes in Iraq
- Postage stamps and postal history of Iraq
- Iraqi resistance
External links
- Schema-root.org: Iraq 178 Iraq topics, each with a current news feed
- War against Saddam The Latest Contributions to the Never-Ending Debate over Just Wars and Unjustified Violence in World Politics
- Coalition Provisional Authority
- Arab Gateway: Iraq
- BBC News Country Profile: Iraq
- CIA information on Iraq
- Indepth Analysis of the Gulf War
- Bush in Baghdad
- Iraq News
- China and Iraq
- On a Small Bridge in Iraq
- Iraqi civilian deaths since start of war in 2003
- The President of the United States of America Proudly Presents: The Official Propaganda for a New Sort of World War
Related Amnesty International links
- Amnesty International Report on Iraq
- Iraq: Tribunal established without consultation
- Iraq: Amnesty International seeks clarification on house demolitions by US troops in Iraq
- Reconstruction must ensure the human rights of Iraqis
- Memorandum on concerns related to legislation introduced by the Coalition Provisional Authority
- Iraq: Forcible return of refugees and asylum-seekers is contrary to international law
| Countries and Territories in Southwest Asia | ||
|
Afghanistan | Armenia | Azerbaijan | Bahrain | Cyprus | Egypt | Gaza Strip | Georgia | Iran | Iraq | Israel | Jordan | Kuwait | Lebanon | Oman | Qatar | Saudi Arabia | Syria | Turkey | United Arab Emirates | West Bank | Yemen |
||
| Countries and Territories in the Middle East |
|---|
| Bahrain | Cyprus | Egypt | Gaza Strip | Iran | Iraq | Israel | Jordan | Kuwait | Lebanon | Oman | Qatar | Saudi Arabia | Syria | Turkey | United Arab Emirates | West Bank | Yemen |